Optimization of Renewable Energy Sources in Smart Grid Systems Using IoT and Machine Learning
Keywords:
- Smart grid, Internet of Things (IoT), Renewable energy, Machine learning, Energy forecasting, Load optimization.
Abstract
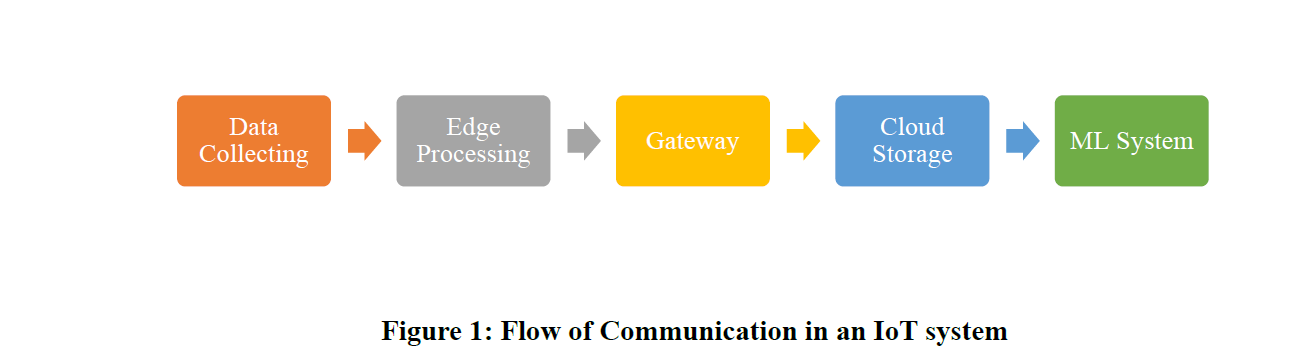
Modern smart grids' use of renewable energy sources offers great potential for enhancing sustainability, efficiency, and dependability in power systems. On the other hand, load balancing and real-time energy management are made difficult by the fluctuating character of solar and wind energy among other renewables. This paper offers a thorough methodology to maximise energy forecasting and load distribution in smart grid systems by combining machine learning (ML) techniques with IoT-based real-time monitoring. Energy metrics were tracked and data sent via lightweight protocols utilising an IoT architecture comprising sensors and microcontrollers (ESP32/Raspberry Pi). While load optimisation was done using Genetic Algorithm (GA) and Particle Swarm Optimisation (PSO), forecasting of renewable generation was done using Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) and ARIMA models. Statistical measures such Mean Absolute Error (MAE), Root Mean Square Error (RMSE), and R² score were used to assess system performance. Results indicated that the suggested IoT-ML integrated framework greatly increased energy efficiency, lowered reliance on fossil fuels, and improved smart grid performance measures including voltage stability, frequency control, and energy loss reduction. The work shows that a feasible route towards the creation of self-regulating, cost-effective, and ecologically friendly smart grids is provided by integrating clever predictive algorithms with real-time data collecting.